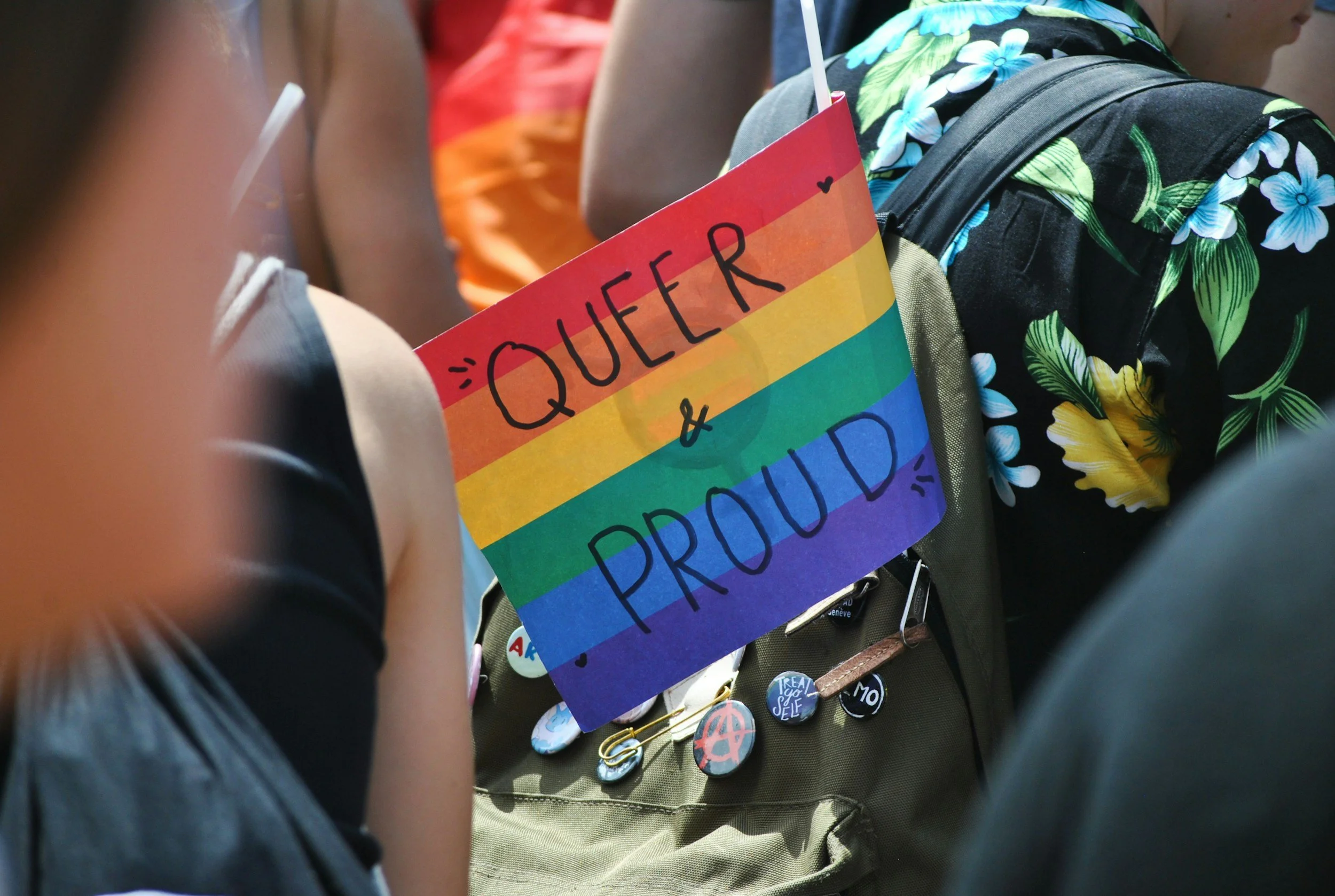Sharing and taking up space in the world – how do we move past a scarcity mindset?
There are 8.3 billion people in the world, and several perspectives on whether this rock is big enough for all of us. If we zoom out, we may have to reckon with a correlation between population growth and the destruction of our home planet, though that might tell us at least as much about a capitalist approach to extracting, creating or sharing resources as it does about an inherent relationship between people and planet. Closer to home, we’re living through a turbulent political time where there is widespread encouragement to view the ways in which we share space and resources with fellow humans through a lens of scarcity and fear. Far-right narratives encourage fear and exclusion of those positioned as ‘other’, prompting many to shrink themselves for the benefit of a wealthy minority intent on claiming more space. I’m interested in exploring the ways that we share and take up our space in the world, and how we might begin to protect against a scarcity mindset in relation to this. Join me on a meander through considerations of sharing space and migration, gender roles, wealth and status, and how social change can begin with looking at things from different angles.
There are 8.3 billion people in the world, and several perspectives on whether this rock is big enough for all of us. If we zoom out, we may have to reckon with a correlation between population growth and the destruction of our home planet, though that might tell us at least as much about a capitalist approach to extracting, creating or sharing resources as it does about an inherent relationship between people and planet. Closer to home, we’re living through a turbulent political time where there is widespread encouragement to view the ways in which we share space and resources with fellow humans through a lens of scarcity and fear. Far-right narratives encourage fear and exclusion of those positioned as ‘other’, prompting many to shrink themselves for the benefit of a wealthy minority intent on claiming more space. I’m interested in exploring the ways that we share and take up our space in the world, and how we might begin to protect against a scarcity mindset in relation to this. Join me on a meander through considerations of sharing space and migration, gender roles, wealth and status, and how social change can begin with looking at things from different angles.
‘There’s not enough for everyone’ is a political choice, not a material reality
There are enough resources globally to meet everyone’s needs. The real issue is distribution - a fact that’s widely accepted but rarely sparks outrage or calls for change. In a predictable ‘tale as old as time’, attention has been diverted away from the few who have amassed enough wealth to eradicate global poverty, and pointed squarely at those who are already marginalised and navigating extreme danger in hopes of eventually reaching safety. The anger and fear being directed at asylum seekers and refugees may not be new, but the context in which it currently exists is. What’s new is the amount of money being thrown at anti-immigration campaigns from domestic and international sources, the technology available to support the rapid spread of disinformation, and the implosion of clearly defined political positioning (see for example, the Labour Party in the UK rushing to make policies that were further to the right on immigration than their Conservative predecessors). Counter-messaging may need to up its game in order to be heard above the well funded and emotive cacophony of hate.
At the risk of entering into a political diatribe about the policing of borders, I feel it’s probably worth addressing the question of how we know when a country is ‘full’, and what decisions are made on the basis of this. There tends to be a dearth of factual information about levels of migration into and out of a country, birth rates, ageing populations, and investment in infrastructure when arguments are being made for further restricting immigration. The intention is to engage people on an emotional level, and it works because of a sense of there not being enough to go around. That seems like an obvious assumption to make when people are choosing between heating and eating, struggling to find work and living in poor housing conditions. When people express fears of overcrowding, it’s almost always an expression of a sense of scarcity regarding public services, job and housing. There may be another conversation to be had about the uneven pressure on services and economies, with more urban areas often experiencing more poverty and issues with infrastructure, alongside a bid to protect what remains of a country’s green spaces from the impact of high human population. There are also inconsistencies around which communities and areas are invested in or neglected. But, ultimately, this issue boils down to economics and political decision making about what is invested in and what is cut.
The UK’s housing crisis persists, even as nearly a million homes in England stand empty or serve as second residences. A ‘lack of social housing stock’ is an expression of political will, not a material reality – social housing stock will exist if the government of the day invests in it. While there may be ‘no magic money tree’, there is an abundance of funding available for things that may be less popular with the voting public, yet more attractive to key political allies (the most obvious and controversial being contributions to wars and illegal occupations elsewhere in the world).
We’re served a sense of inevitability about this system, which likely makes us feel powerless. The people making political and economic choices are too powerful to be stopped – the mega-rich can get away with anything if they throw enough money at the problem. So, where does that leave us? Perhaps in search of someone else to take the fight to – someone we can win against. This is how despots have used scapegoating to redirect anger towards a vulnerable minority throughout history, and apparently, it still works.
If we feel confident that it’s possible to fairly distribute resources and access to public services (which are disproportionately staffed by ‘immigrants’) among all those who need them, we have no reason to fear losing what we have to anyone newly arrived. What reframing would it take to believe, and behave as if, there is actually enough space and resource for all of us? This is a conversation I’d like to hear in political spaces.
Taking up your space – how we embody or resist our assigned roles
I’ll be honest – this piece began in my head as a rant about ‘manspreaders’, and later morphed into something a little loftier about how humans negotiate sharing space in the world. London commutes in recent years have seen me choosing passive aggressive sighing over potential confrontation (or having to touch the offending manspreader). For the uninitiated, the term ‘manspreading’ refers to men taking up more than their allocated amount of space in public by sitting with legs spread wide in what seems reasonably interpreted as a show of casual dominance. It’s a minor issue on the face of it, but I’m interested in the ways in which we embody the roles we’ve been given in life via the accident of birth, and the interplay between how much space we feel entitled to take up and social hierarchy. This is not a new concept - feminist and anti-racist discourse has had much to offer about the idea of shrinking ourselves to avoid appearing threatening to those who hold a kind of social power that, on some level, they know is fragile. That fragility can be dangerous, and so those of us in female, Black, Brown, queer, trans, disabled and other marginalised bodies often learn – consciously or unconsciously – to make those bodies as small and convenient as possible when faced with potentially dangerous situations. And of course, there has been a tennis match of backlash in response to this – one notable example being the game of ‘patriarchy chicken’ that some women have documented as a way to test how often they would collide with men while walking in public if they didn’t give way to them (spoiler – the answer is ‘very often’).
I’m concerned and curious about the ways in which social divisions and a return to restrictive ideas about gender might calcify some of these embodied expressions of role and power, and the potential for violence as a response to non-conforming self-expression and claiming of space. This policing of norms, bodies and entitlement to space in the world comes straight from the fascist playbook. And while I don’t want to advocate for anyone to put themselves at risk of harm, I feel that we must continue to work on taking up our space in the world, letting others take theirs, expressing ourselves authentically, and pushing back on archaic roles and power dynamics.
Lawns, legroom and lobbies - social hierarchy in measurable terms
Literal space in the world, in the form of land, has been available to acquire through purchase or invasion throughout most of human history. This is a concept that might feel inevitable, in spite of its absurdity when we zoom out from it. We exchange our labour for currency, a human construct that (in contemporary times) fluctuates in value according to the whims and anxieties of professional gamblers. We hope that this exchange of labour and currency will allow us to say that a slice of the planet we live on belongs to us to do with as we please (local planning regulations permitting). The more value our labour is deemed to be worth by mysterious market forces and the social structures that influence them, the more space we are permitted to occupy. The value assigned to specific forms of labour doesn’t necessarily bear any relation to its social or environmental impact – what’s valued most is potential for further economic growth. So, taking up a lot of space in the world may be considered to be a reward for contributing to companies’ profits and the overall profits made on of a larger patch of land.
In contemporary society, buying a space to call home is increasingly inaccessible. For many of us, the aim is to take up the space that we need in order to live a comfortable and peaceful life. But the number of square feet we can call our ‘own’, and other forms of entitlement to space have also been status symbols throughout history. Take, for example, the humble suburban lawn. This patch of trimmed grass isn’t traditionally designed to support biodiversity, to grow food, or even necessarily to be occupied by its owners. It’s often an extension of the home that is maintained and observed, but doesn’t offer much functionality. Lawns originated as status symbols among the upper classes and, even today, modest lawns serve as displays of wealth—often in climates ill-suited for them. The point of this example is not to berate anyone who meticulously maintains a small patch of grass, but to step back from social norms and markers of status and look at them with curiosity. Disentangling ourselves from the idea of inevitability in the ways we organise our lives (both in private and in community) offers an opportunity to start imagining how things could be different, and what we might want that to look like.
Another example of this ‘space as status symbol’ phenomenon is the hotel or corporate office lobby. These are spaces whose practical function doesn’t necessarily tally with their square footage or their grandeur. They exist to let people know immediately that they are entering a prestigious, important and/or expensive space. The impact of this may be a sense of importance, power and belonging, or a feeling of exclusion (if not, in some cases, a more literal experience of exclusion). We can communicate a lot about who is or isn’t welcome in a space, and how we would like them to feel, through the ways in which we present and organise that space. This is not news to designers, architects, or city planners, but may be a consideration to bear in mind for those of us creating spaces that we wish to be welcoming and inclusive, often on a far more modest budget than a luxury hotel owner.
And now, to air travel… Each time I’ve flown over the last few years, I’ve found myself expressing the same frustration. I’m a pretty small person, but I’m convinced that the amount of space available to me on economy flights is reducing a little with every trip (no, it’s not me expanding). The shift of functional services and relative comfort from standard to premium is a common feature of life in the 2020s. This reminds me of ‘enshittification’ - a corporate tactic of initially offering quality before degrading it and raising prices, while pushing competitors out of the market. A version of this applies to leg room and seat space on flights. I remember complaining about having splashed out for ‘economy plus’ on a flight and apparently being put in a cramped economy seat. When the actual economy seats in the back half of the plane were pointed out, I was reluctantly glad not to be a six foot person who’d spent upwards of £1000 to be crammed into a child sized seat for eight hours. This was an airline I’d flown with a few years previously, and the difference was jarring. What’s interesting about this is the sense of scarcity and acceptance of declining standards around access to space and comfort. In a struggling economy, companies will take whatever action they deem necessary in order to stay afloat, including packing people into spaces like sardines. I’m curious to see how far we will go in accepting the widening division between those who can afford comfort, space and functional services (both commercial and public), and those who have their access to experiences cut off or limited by miserable conditions, long waits and increasing inconvenience. Since my expertise lies in the social, rather than the economic field, it’s difficult to imagine an effective solution for this. But I’m interested in what progressive and creative experts have to say on the matter, and I’m aiming to stay curious about what’s possible, rather than let my lack of knowledge lead me back to a sense of powerlessness and inevitability.
Abundance mindset – what looks different through this lens?
With all of these weighty social issues in mind, it might feel overwhelming to tackle questions of what’s possible as an alternative to a competitive, fear based approach to sharing the world with other humans. We’re not going to revolutionise embedded systems and perspectives easily, quickly or singlehandedly. But if we zoom all the way back in to our own thought processes (and how we communicate them to others), there is a starting point that could be both achievable and encouraging.
I’m using the concepts of ‘scarcity mindset’ and ‘abundance mindset’ here as a way to frame different ways of looking at the world. But I don’t use them uncritically – these are ideas that might lend themselves to over-simplification and stigmatising people for their experiences of structural inequality, so it’s important that they’re offered and considered with nuance and an acknowledgement of the two way relationship between how we think and the systems and cultures we are living in.
A scarcity mindset tells us that there is not enough to go around – this may be about physical space, housing, food, public services, jobs, money etc., but also may be applied to more relational concepts like power, love, being seen and heard, time and attention. If our baseline is a sense of scarcity, an obvious survival response may be to fiercely guard our resources, shut others out and compete for more. We might need to tell ourselves or be told various stories in order to position this as ‘fair’ and maintain our sense of ourselves as ‘good people’. Even though we’ve evolved to survive through cooperation, the amygdala-driven instinct to narrow our focus for our own survival can be powerful, hence populists successfully connecting with this response in disillusioned people, no matter how many times we say ‘never again’.
Conversely, an abundance mindset is similar to a growth mindset, in that it assumes that there is enough to go around and that we have the capacity to access the resources we need. It’s a focus on the possible, which tends to encourage us towards action because it positions us as powerful. It’s easy to see why economic crises, oppression and deteriorating living conditions make it harder to cultivate an abundance mindset – in these situations, evidence, experience and exhaustion tell us that we’re not powerful, and that resources are scarce and inaccessible. Spending the time and energy on reflecting and cultivating an abundance mindset might feel like a luxury when we’re in survival mode. But perhaps it’s a good, preventative practice to get into before we hit survival focused tunnel vision. Change starting with a belief in what’s possible is a cliché, but also an important aspect of human psychology. One of my favourite coaching questions is ‘what would you do if you did believe [insert relevant growth focused belief]?’ Imagining and outlining the steps towards a goal doesn’t guarantee success, but it’s a good starting point from which to look for ways around barriers, keep motivation alive and catalyse change. I’m not advocating for some bootstrap capitalist approach (no doubt, that’s obvious from the mini manifesto above) – it’s not about the power of the individual to improve things for themselves. It’s about taking the time, space and energy to reimagine what sharing the world with others could look like, even when time, space and energy feel scarce. And sharing ideas and imaginings with others may be another step towards changing things for the better – as interdependent creatures, we have so much capacity to make apparently impossible things happen when we tackle them together.
‘You’ve got to fight for your right to party’ – balancing accessibility and momentum building in a time of social isolation
Recently, I travelled a few hundred miles to one of the three cities I consider to be a ‘home town’, in order to host a party marking a new chapter in my life. The tricky decision making process about how many people to invite, what venue to hire, what food to provide, what time of day to gather, and anything I could do to make showing up easier and more enjoyable got me thinking about how we get people together and make things happen in this peculiar moment in history. I’m starting from an assumption that it’s harder than it used to be to bring people together in person, whether in a social setting, on a group programme or for a community event. It's important to explore and challenge this assumption, though the struggle to assemble in the 2020s is a fairly established concept.
Reflecting on my own experiences of being a host, facilitator or participant, I’ve been wondering about how we can strike a balance between creating spaces that respect and accommodate people’s complex lives, depleted energy levels and access needs, and eliciting commitment and participation at a time when it seems like we need strong community more than ever. Of course, this may be a more crucial question when applied to building movements than in relation to party planning. But community and connection take many forms, and we are living in a particularly fractured time, with lasting impacts from Covid lockdowns, healthcare and economic crises, and safety concerns for many as we descend into scary political territory. So perhaps it’s worth considering how we get people together for whatever reason in this difficult context.
Recently, I travelled a few hundred miles to one of the three cities I consider to be a ‘home town’, in order to host a party marking a new chapter in my life. The tricky decision making process about how many people to invite, what venue to hire, what food to provide, what time of day to gather, and anything I could do to make showing up easier and more enjoyable got me thinking about how we get people together and make things happen in this peculiar moment in history. I’m starting from an assumption that it’s harder than it used to be to bring people together in person, whether in a social setting, on a group programme or for a community event. It's important to explore and challenge this assumption, though the struggle to assemble in the 2020s is a fairly established concept.
Reflecting on my own experiences of being a host, facilitator or participant, I’ve been wondering about how we can strike a balance between creating spaces that respect and accommodate people’s complex lives, depleted energy levels and access needs, and eliciting commitment and participation at a time when it seems like we need strong community more than ever. Of course, this may be a more crucial question when applied to building movements than in relation to party planning. But community and connection take many forms, and we are living in a particularly fractured time, with lasting impacts from Covid lockdowns, healthcare and economic crises, and safety concerns for many as we descend into scary political territory. So perhaps it’s worth considering how we get people together for whatever reason in this difficult context.
Let me offer a caveat. I don’t want to use this as a platform to complain about being inconvenienced or upset by people not showing up for things, nor as a way to question whether progress towards more accessible spaces and communities has ‘gone too far’ – in most situations, accessibility has not gone nearly far enough. I’m interested in our changing social contracts, the impacts of technologies on how we plan, communicate and socialise, what it might mean if we’re all too exhausted to get together, and how we address these challenges in a way that honours people’s autonomy, need for downtime, and variable or limited capacity to consistently take part in community life.
And so, to the challenges of planning parties, meetings, training sessions, workshops, community events and so on. The rule in 2025, I’m told, is that we should expect around 50-75% of an invite list to say yes, and around 50% of that group to show up on the day. This seems to be surprisingly accurate a lot of the time, though it’s not something we can rely on in the planning process - who wants to risk being the host who only provided for half of the people who RSVP’d ‘yes’, only to find that everyone actually shows up? In my experiences of both facilitating and attending events in the last few years, there is a marked difference from expectations pre-pandemic in terms of attrition rates. Last minute apologies often come in a flurry, especially if someone starts the process of responding publicly on a chat thread or group invite. It can seem as if a handful of people sharing their (entirely reasonable) stories of exhausting days, heavy workloads or babysitting issues gives anyone on the fence about attending an event the green light to cancel. I’d hate to live in a world where people felt pressured to attend a meeting, party or group session, no matter the emotional, physical or financial cost. And I also wonder how our ability to show up has been shaped by a world that’s hyper-individualised, and full of endless choice about what to buy, where to go and what to engage with (all filtered through algorithmic curation by billionaire owned tech platforms).
How might we be influenced by a culture offering so many options that we find ourselves exhausted and in decision paralysis? I remember considering this in my first few years of living in London, during and after Covid lockdowns. The experience of being newly resident in one of the world’s mega-cities was surreal at a time when I could only explore my immediate surroundings for an hour a day. Later, it was equally surreal and overwhelming to find that there were countless events, groups, places and experiences available to me at any given time. I eventually found activities and groups that I was able to integrate into my weekly routine, but otherwise dipped in and out of communities, political organising, and recurring activities fairly inconsistently. I suspect this may be a feature of life in a big city at a time when communication technology and good public transport links make it possible to find just about anything we’re interested in, and to unconsciously assume that all of these opportunities will still be there next time if we miss out today. It seems that being in large group spaces also became more energetically costly during recent years - our post-pandemic relationships to the risks and compromises of sharing physical space form part of the changing social landscape. There have been many times in the last few years when I’ve been faced with a choice between stretching myself to face a sweaty, crowded London commute to gather with people for something that would bring me a sense of purpose, connection, energy, catharsis or joy, and staying in my comfort zone at home, with the option of quietly recharging my batteries or doing something requiring minimal social effort. I’ve almost always felt better for choosing to stretch myself if I’m able to, and happy with my decision to have a recharge day if I genuinely need one. But there have been other times when I convinced myself to avoid something I’d been looking forward to because I was apprehensive about meeting new people, or didn’t want to travel, only to find myself later wishing I had. One example of this is an embodiment group that I’d hoped to be involved in developing with some peers. Life took me in an unexpected direction, and I stepped back for a while. When I found myself more available, I struggled to build a routine of attending consistently, but hugely valued the sessions. I was disappointed when the group inevitably ended due to a lack of participation, but had to acknowledge my part in that.
Conversely, I’ve found that I respond well to activities with built-in accountability when it comes to building routine and making commitments. I appreciate the clear expectations, and also the discretion and flexibility of attendance and cancellation policies offered by some groups I’m part of - they’re not designed to prevent people with inconsistent health or life challenges from being able to meaningfully participate, but they lay the groundwork for enough consistent participation to allow progress towards a goal, or a critical mass of participants. It can feel like an uncomfortable wielding of power or boundaries to implement something like this, especially at a time when we’re more conscious of each other’s needs and challenges. But if we’re able to self-advocate, negotiate and offer flexibility within these boundaries, perhaps it’s less necessary to avoid setting them. I wonder whether living in curated bubbles that cater to individual needs and desires via an array of goods, services and personalised settings has made our comfort zones so enveloping and enticing that we have diminishing levels of incentive to step outside of them into a world that may involve risk, inconvenience, over-stimulation, and also growth, connection, challenge and learning. At the risk of falling into a ’back in my day’ cliché, I can’t help thinking about the contrast between making and carrying out plans in a pre-smartphone era and doing so today. I’m not the first to notice the impact of being able to fire off a quick message half an hour before an event to offer an apology without having to look the recipient in the eye, and with the assumption that the message will be received in time because we expect each other to be tethered to our devices by default. I’m grateful for the obsolescence of the communication fails I occasionally experienced as a teenager (e.g., a friend and I waiting for each other at different branches of the same city centre coffee chain, resulting in some comedic pay-phone relay calls to each other’s parents). And, while I appreciate living in a more convenient world, I must admit to a pang of nostalgia for the expectation that a plan would go ahead because there was no easy way to change last minute without knowingly affecting whoever was waiting for us. Maybe this nostalgia signals a new phase of life for me, as a member of the last generation to spend our childhoods without 24/7 online connection and then enthusiastically adopt it in early adulthood. Regardless, I find it interesting to reflect on the ways in which technological and social changes are inextricably linked, and shape our social contracts.
When I’ve had friendships or professional helping relationships with people whose health makes it difficult for them to reliably show up, there has been a clear and direct message from many of them – ‘please keep inviting me’. One resident at a housing project where I offered wellbeing support said ‘I really appreciate you inviting me to sessions, even when I don’t respond. Please don’t give up on me’. That was a powerful reminder of the tenacity required to keep trying to build a shared space in the face of barriers and challenges. And yet, there are finite resources (including energy and tenacity), as well as minimum levels of participation required in order for most projects to work. I’ve been disappointed when courses I’ve enrolled in have been cancelled because there weren’t enough participants. But it happens - sometimes the timing is wrong, and sometimes, the challenges with getting bums on seats tell us something about the economic or political climate that it’s worth paying attention to. This is the main reason that I’m refocusing a significant proportion of my work from private client contracts to funded programmes that are more accessible to those who need them most. Some programmes I offered saw a disparity between interest and participation because people who needed the input weren’t able to make the investment at that time. It felt important to respond by considering how to meet people where they are.
This doesn’t neatly answer the question of how we might meet people where they are, if where they are is a place we can’t find a way to reach. And of course, there isn’t one right answer. Something I’m working on is not taking others’ non-participation personally. It’s true that a last minute drop in numbers for an event or programme might have an impact on resources, plans and dynamics, but the challenge is to keep perspective. It’s easier to learn about what has worked and what could be done differently next time from a place of curiosity than from feelings of rejection. Sometimes, meeting people where they are involves continuing to invite them to let them know that they are valued, even if they never show up. Often, clearly addressing access needs, preferences and anxieties experienced by people who are new to a space or group can improve participation. And in some contexts, agreements about accountability and commitment levels are necessary to ensure that enough people consistently show up to keep an activity or movement alive. I find myself returning to the same question in many of my posts - where is the balance of individual and collective responsibility here? There are many things that a collective, or those with responsibility for hosting events can do to meet as many participants’ needs as possible. And there are things we can do as individuals in order to contribute to a world where communities grow and thrive, and where in-person, embodied gatherings remain viable and accessible. I’m enormously grateful for the way that meeting virtually has opened up opportunities and connections to people regardless of location, health or mobility. I’m also someone who often needs time to recharge my social battery, an experience I share with many of my friends. So, I understand that we won’t solve society’s problems and improve our own wellbeing just by pushing ourselves to spend more time in groups. And yet, in this particular moment, where billionaires stand to benefit hugely from our isolation and exhaustion, it feels like an act of resistance and social change to find ways to step out of our curated comfort zones and into community.
LGBTQIA Pride – Authentic Expression and Being Seen, Heard and Valued All Year Round
As we reach the end of Pride month, I want to reflect on what the concept means to me, the importance of being able to show up authentically, and the need to create spaces where people feel seen, heard and valued to continue all year round. Like many in the LGBTQIA community, I’ve developed a level of cynicism about the corporate pinkwashing that characterises parades and parties that have their origins in civil disobedience and resistance to oppressive laws and discrimination. It’s a complicated picture, because on one hand, I feel extreme discomfort about marching alongside corporations involved in the arms trade, institutions that are being investigated for horrific abuses of power, and more run-of-the-mill big businesses that will drop the concern for their queer and trans colleagues the moment they change their social media banners from rainbow flags back to ‘normal’. But on the other hand, I’m well aware of the need for visibility, for antidotes to shame and stigma, and for spaces where we can show up authentically and unapologetically.
(Content warning – hate crime, discrimination, homophobia, transphobia, serious violence)
As we reach the end of Pride month, I want to reflect on what the concept means to me, the importance of being able to show up authentically, and the need to create spaces where people feel seen, heard and valued to continue all year round.
Like many in the LGBTQIA community, I’ve developed a level of cynicism about the corporate pinkwashing that characterises parades and parties that have their origins in civil disobedience and resistance to oppressive laws and discrimination. It’s a complicated picture, because on one hand, I feel extreme discomfort about marching alongside corporations involved in the arms trade, institutions that are being investigated for horrific abuses of power, and more run-of-the-mill big businesses that will drop the concern for their queer and trans colleagues the moment they change their social media banners from rainbow flags back to ‘normal’. But on the other hand, I’m well aware of the need for visibility, for antidotes to shame and stigma, and for spaces where we can show up authentically and unapologetically. And some might argue that pinkwashing is preferable to the alarming experience of seeing companies retract their public support for the LGBTQIA community through fear of upsetting powerful bigots.
Recently, working with people whose experiences of being LGBTQIA in their home countries were shockingly full of trauma and danger reminded me of how important it is to have public, joyfully resistant declarations of welcome and inclusion. And seeing queer or questioning kids attend their first Pride is always a humbling and beautiful experience that makes me so happy that they’re not growing up in times like so many of us did (Section 28 – the UK law that banned public sector bodies from discussing or ‘promoting’ LGBTQIA identities – lasted for my entire school career).
So I begin this reflection with a word of caution that’s repeated by tired members of the community every year. Performative allyship, and enjoying the glitter without engaging with the struggle that necessitated marching through cities, yelling ‘we’re here, we’re queer, we’re not going anywhere!’, isn’t helping. It’s great to show solidarity and be visibly supportive, but stigma, lack of access to healthcare, transphobic public policy, homophobic hate crime and poorer mental health outcomes (to name but a few) don’t go away when the flags are packed away for another year and the queens get out of drag.
I’m not advocating for getting rid of marches and celebrations altogether, but I’m more interested in grassroots, community level organising and thinking about how we can create spaces all year round that are based on a real desire to support people to show up authentically and know that they are safe, welcomed and valued. An intersectional approach is crucial, so it feels important to say that I’m not imagining these spaces with only the LGBTQIA community in mind. Apart from anything else, we contain multitudes and might have several minoritised identities that mean facing very specific barriers to access and forms of discrimination. I’d like to take some space to think about what those spaces might look like – what values, action and principles might be involved, and how it feels to be part of them.
When I think about what stands out to me as the important elements of Pride month that I’d like to see honoured throughout the year, the first words that come to mind are resistance, representation, rememberance and reimagining. Some of this might be at odds with the shiny, corporate approach to celebrating Pride, though I’m curious about how the idea of disrupting or ‘queering’ these spaces, at least as a first step towards deeper change.
Resistance
I had a great time at last week’s Dyke March in London, with ‘The First Pride Was A Riot’ scrawled in sharpie across the back of my jacket. This was an event that did a great job of showing joyful resistance – a combination of power, playfulness, euphoria and outrage. It encouraged us to stay connected to the origins of the Pride movement, and what we’re marching for. Maybe some of the people who show up to wave at the floats and watch the performances in their home town each summer would be horrified to think of trans people throwing bricks during the Stonewall riots, but that was the origin of today’s movement in all its shiny, corporate glory. And I hope they would also be horrified by the police brutality and human rights abuses that led to that riot in the first place. If this all seems like something that happened in a bygone era, and perhaps not so relevant today, I’d suggest that we’ve come a long way with so many rights and freedoms, and that the backlash against that progress is very real and very frightening. Keir Starmer, likely the next UK Prime Minister, has recently stated that he is against the teaching of ‘gender ideology’ in schools, effectively signalling a return to something akin to Section 28. And looking at equivalent developments in the USA and in European countries (such as restrictions on lesbians’ right to adopt in Italy) shows how easily things can change for the worse. It’s therefore essential that we protect our ability to speak truth to power, to show up in public as our authentic selves, and to protest injustice. Beyond LGBTQIA issues, there are threats to our civil liberties and freedoms creeping into our societies, and we must be able to find strength in numbers and resist. There are related ideas that we can extrapolate from this in terms of community building and organisational development too – essentially that it’s dangerous to hold too tightly to rigid and traditional hierarchies where people are afraid to speak up.
Representation
To return to the subject of Section 28, I often think about the impact of having little to no meaningful representation of people whose sexual orientation and gender identity I could relate to throughout my childhood. I didn’t understand my own identity for a long time, having had my formative years influenced by enforced silence on the subject of LGBTQIA identities, bodies and reelationships. I realise that there were many people in my generation who were joyfully, defiantly queer in the face of all of this, and who couldn’t deny who they were if they tried. But no doubt, there were at least as many of us who were confused, ill-informed and dealing with a nagging suspicion that something was ‘wrong’ about us and that it wasn’t a good idea to talk to anyone about it.
It's perhaps a cliché to say that representation matters and that ‘if you can see it, you can be it’. But there’s also a lot of value in considering who is visible in a space, a role, a community, or a position of power, and what that might do to welcome or discourage people from attempts to be part of the community, or pursue a role. It’s also worth pointing out that people who may have had to develop hypervigilant levels of sensitivity to signs of safety/danger tend to be pretty good at seeing through tokenistic attempts to ‘tick the diversity box’. Again, going through the motions from a place of compliance isn’t going to contribute much to meaningful change. But for young people, and former young people who didn’t see themselves represented in the past, seeing positive examples of people like themselves in spaces and communities can have a genuinely positive impact.
Remembrance
Pride is, in part, a celebration. But it’s also an opportunity for us to commemorate those we have lost, to remember where we’ve been and how far we’ve come, and to use this to inform ongoing action towards further change. I’d suggest that this approach, which locates us in time and place, and offers opportunities to learn from our mistakes, is a crucial part of any social movement or community. Some of the injustices and tragedies that have taken place, and continue to take place, within the LGBTQIA community are almost too overwhelming to comprehend. Losing so much of an entire generation during the AIDS crisis in the 1980s seems to have had a fairly significant impact on intergenerational learning and younger people’s engagement with their community’s history. Part of me is relieved for queer kids growing up in more recent years, perhaps being able to take many of their rights for granted, or to be unable to imagine what it might have been like not to have them. But there’s a risk of not learning from the past, not honouring those who fought for human rights and those who lost their lives, and becoming complacent. We don’t have to look very far to see how quickly and easily hard-won rights, laws and policies can be revoked, and how successfully minority groups can be made into scapegoats to distract from abuses of power. And we don’t have to look far to find very recent examples of the loss of lives as a result of violence and discrimination – I’ll be remembering young people like Brianna Ghey as I march tomorrow. These are difficult and sobering thoughts, though remembering those lost and those who came before is the least I can do in a bid to connect with our shared history.
Reimagining
It’s often the case that ideas and ways of being move from the margins to the centre, only for something new to appear outside of the norm and eventually influence mainstream culture (and/or perhaps be assimilated into it – though assimilation is a topic in and of itself). I believe that the world has a lot to learn from queer culture, and pushing the boundaries of ‘respectability’ is potentially helpful for everyone. Similarly, the stigmatising of certain bodies and what people do with them has done, and continues to do, serious harm – pushing back against this with radical inclusion is necessary and important as part of a move away from categorising some bodies as inherently better than others. Equally, we can all learn from the freedom that comes from ways of relating to each other without there being a script or template that we’ve been primed for throughout our lives. For example, how do we work out the division of labour in households where the usual gendered expectations don’t apply? Well, generally we might work it out according to ability, preference, need and so on, as opposed to social expectations based on chromosomes. I’m being a little flippant, and I realise that many people of all genders and orientations are entirely capable of non-stereotypical negotiations, but the point is that there’s freedom and a chance for Adult-Adult communication when we don’t have so much baggage from social pressures and norms. And I’d like that to be extended in so many ways beyond the LGBTQIA community – for us to reimagine what spaces and communities free from inherited and restrictive notions of gender, relationships and identity might look like. What would it be like if we all had the resources that helped us to develop the skills to work out exactly who are and what we need, and if we all felt safe enough to show up courageously and authentically everywhere we went? I hope these are questions to reflect on as we imagine what’s possible going forward, and I want to offer my gratitude to the LGBTQIA community for offering me welcoming spaces to work out who I am and show up as myself.
Essential Skills for Socially Conscious Leadership - Using the Seven Cs Model to Drive Change
In recent years, there’s been a cultural shift in many parts of the working world, from top-down, ‘command and control’ leadership to more socially conscious, collaborative approaches to leading teams. For some, this may still be seen as a fluffy optional extra or an invite to waste precious time by crowd-sourcing decision making processes. But I’d argue that developing leaders who are emotionally intelligent, skilled communicators with good boundaries and socially conscious values is a necessity, not an option. Even now, it’s often still the case that career paths can involve becoming proficient in a specific role, then being promoted into a leadership role on the strength of experience that may or may not require good people skills. If organisations don’t invest in supporting emerging leaders to develop the relational skills necessary to support healthy, happy, successful teams, they risk their people’s wellbeing, the quality of their work and the potential for innovation and creativity. So, what are these skills and why are they important?
In recent years, there’s been a cultural shift in many parts of the working world, from top-down, ‘command and control’ leadership to more socially conscious, collaborative approaches to leading teams. For some, this may still be seen as a fluffy optional extra or an invite to waste precious time by crowd-sourcing decision making processes. But I’d argue that developing leaders who are emotionally intelligent, skilled communicators with good boundaries and socially conscious values is a necessity, not an option. Even now, it’s often still the case that career paths can involve becoming proficient in a specific role, then being promoted into a leadership role on the strength of experience that may or may not require good people skills. If organisations don’t invest in supporting emerging leaders to develop the relational skills necessary to support healthy, happy, successful teams, they risk their people’s wellbeing, the quality of their work and the potential for innovation and creativity. So, what are these skills and why are they important?
One framework that might be helpful in defining good social leadership is the ‘7 Cs’ – part of the social change model of leadership development created by the Higher Education Research Institute of the University of California Los Angeles. This model highlights that anyone can develop these qualities and be a leader, regardless of their position in a hierarchy. It identifies seven qualities and skills that socially conscious leaders need to have in order to succeed. They are:
Consciousness of self
Self-awareness is an important starting point in any successful endeavour, especially as it relates to being and working with others. Understanding our own preferences, needs, areas for growth and development and communication styles can help to prevent misunderstandings and conflict, as well as supporting each person in a team to play to their strengths. Of course, being aware of our own needs and preferences is only the beginning of the story. I’ve often encountered examples of leaders and teams taking quizzes to determine their communication preferences, personality structure or archetype, only to then use their findings as a way to absolve themselves of unhelpful behaviours and responses – ‘what can I do, I’m a [insert category here]!’ Don’t’ get me wrong, I’m not here to denigrate any of these categorisations – they are as useful as their application. Ideally, self-awareness will be an impetus for further personal development, asking for support where needed, and negotiating with others about how to get the best from communications with us. When I was training in Performance Psychology, my supervisor had me develop what was essentially a ‘how-to’ manual that explained the quirks, needs and preferences that might help others to work well with me. I’ve never handed over the physical document to a new contact (perhaps a slightly overwhelming prospect). But it has often been helpful for me to explain to people I line managed that, for example, my brain needs time to transition between tasks, and as such, if I’m focusing on a task and am interrupted unexpectedly with a request, my initial response might be a blank stare or a clipped tone. I’ll generally manage to mentally change gear after a minute or so, but I’ve found that it’s kinder and more efficient to negotiate ways to check my availability for a chat, rather than launching into a discussion of which I’ll miss the first few sentences. This doesn’t mean that I have no responsibility to do my part in getting the most from both my brain and my relationships with colleagues, but in this case, the thing I’ve developed an awareness of and communicated to others is related to an ADHD trait – it’s not something I can easily change. That is to say, sometimes we can become aware of a tendency, communicate it and realise that we need to make a change within ourselves. And sometimes, it’s enough to develop the awareness, communicate a need and negotiate a workaround.
Congruence
This is a core concept in many therapeutic schools of thought. It’s about honesty, integrity and alignment of thoughts, feelings and behaviours. We are social animals, evolved to be (for the most part) sensitive to social dynamics and signs of potential conflict. As such, many people are at least subconsciously aware that something feels ‘off’ when someone is being inauthentic. When our language, behaviours, body language, micro-expressions and signs of energy levels seem to contradict each other, trust can be eroded. This might call to mind the debate about ‘bringing your whole self to work’ and how much authenticity is appropriate in specific work related situations. We often have a concept of ‘professionalism’ which suggests that we should leave our real emotions and thoughts at the door in favour of a more polished version that carries less risk of conflict or discomfort. I’m a fan of diplomacy, professional boundaries and appropriate challenge, and I don’t think these are particularly at odds with an approach to leadership that gives permission and encouragement for leaders to be unashamedly human, with emotions, flaws and the ability to come back from making mistakes. This permission can help us to cultivate more congruence – we might feel more able to say things like ‘I’m really sorry – I do want to help you with this but I’m a feeling bit overwhelmed with working on task x and might struggle to give you my full attention right now. Can we find a time where we can sit down and really get stuck into problem solving the issue?’ or ‘I’m noticing a bit of resistance in myself as you talk about this idea. I think I need to go away and explore what that’s about – I don’t want to shut you down. Can you give me a bit of time to ponder it and then we can discuss it again over a coffee later today?’
Commitment
This seems like an obvious point in the context of good leadership, but commitment to the cause is essential. Given that, as previously mentioned, we’re all human, there will likely be times when we feel less motivated or more overwhelmed with our work and find it difficult to connect with our commitment. There’s a real watch-out for burnout here – if we begin to feel a sense of apathy and disconnection from the mission, vision and values we’re working towards, and struggle to find compassion for the people we’re supporting, we need to listen to the warning signs and take action (including the sort of action that leads to taking genuinely restorative breaks). But when not at risk of burning out, it’s important for leaders to be able to find and demonstrate motivation and some level of passion for their work. Personally, I was never especially passionate about management roles in and of themselves, but I’ve always loved supporting people to develop and recognise their skills, find their passion and bring their unique skills and insights to their work. I loved using a coaching approach in my leadership work, even before I trained as a coach. That passion offered enough leverage to get me through the aspects of management roles that I found less inspiring. Even in leadership contexts where the commitment isn’t related to the core activities of a business or organisation, a deep commitment to supporting people is essential.
Common purpose
Ideally, establishing shared values and purpose begins at recruitment. And it falls to leaders to support others to connect to that sense of purpose, particularly when things are feeling difficult or stuck. This can link back to congruence – it’s worth interrogating and discussing how (and indeed, if) an organisation or team’s stated values and purpose actually live beyond the pages they’re stated on. And there may be a need to establish a set of specific values, aims and purposes beyond those of a wider organisation – what do people really care about, feel motivated by and want to get out of a project? Again, the concept of leverage is often useful when motivation is low or it seems there is no end in sight – how can we connect with the wider purpose and the reasons behind our efforts? There are a couple of caveats attached to this, however: firstly, it’s important not to abuse or over-use this tactic in a bid to push people beyond what can reasonably be expected of them. Having spent around two decades working in the third sector, I’m very familiar with the ways that people’s passion for social justice can be exploited and used as a reason for being overworked and underpaid. And secondly, it feels important to inject a little realism (or perhaps cynicism?) about the realities of the working world for many people. We live under a capitalist system for the time being, and selling our labour is necessary for survival. Not everyone takes on a job out of a sense of passion for a cause, and many people prefer to show up, tackle the tasks at hand, and go home to enjoy the remaining hours in their day. So I’m not suggesting that we need everyone to demonstrate commitment to a shared purpose at all times; but if we’re thinking about the sort of work that asks for shared values and commitment to a cause, establishing a good fit at recruitment and support to connect to purpose are key. A final watch-out here is conflating shared values with groupthink – while it's important to have everyone pull together in the same direction, conformity and a restrictive sense of ‘culture fit’ can really deprive a team of diverse perspectives.
Controversy with civility
This is about appropriate challenge and leaning into discomfort without creating a hostile working environment. It’s a difficult thing to achieve and, I believe, very much worth investing the effort into. As mentioned above, a sense of common purpose doesn’t negate disagreement, conflicting needs and challenge. These will inevitably arise (and if not, that may present its own set of concerns to be addressed), and how leaders respond and help to cultivate a safe enough environment to contain them is crucial. I’ve found myself in groups of leaders where the majority view was that challenge and disagreement were negative and to be avoided at all costs. I found this deeply uncomfortable, as it seemed obvious to me that this would likely lead to festering resentments, a lack of congruence and missed opportunities for learning and growth. I’m very committed to creating environments where difficult conversations can be held with compassion and curiosity… and yet, I’m also quite conflict avoidant, so I understand the urge to smooth things over, rather than get them out in the open. I believe that good social leadership involves being grounded, compassionate, sensitive and robust enough to make and discuss difficult decisions, to hear challenge from a place of openness, to speak up when something feels wrong or unjust and to encourage others to do likewise. ‘Civility’ in this case isn’t about polite avoidance, a stiff upper lip approach or an aversion to disagreement; but rather, might involve things like the use of ‘I statements’ (where we take responsibility for our own reactions to others and start with describing our own feelings, e.g. ‘I feel frustrated when you keep missing and pushing back this deadline, because it stops me being able to do my next task. I’d prefer it if you could give me an honest assessment of what’s getting in your way, whether you need any additional support, and when you realistically will be able to get it done’). It might involve unpacking our own sense of defensiveness when we’re challenged and taking time to formulate a more thoughtful response. It might involve some reflective work around your organisational culture around challenge and controversy.
Collaboration
Collaboration has become something of a buzzword over the years, and with good reason. There are levels of collaborative work, from consulting with and incorporating others’ ideas and views into planning a project, right through to structures with flattened hierarchies and equal decision making power. But the spirit of collaboration in any context is about genuinely valuing each person’s contribution, understanding the benefits of bringing different ideas, perspectives, experiences, skills and ways of working together, and making space for others. Sometimes, collaboration can be the most effective, efficient and energising way of working, because it can allow people to draw on their strengths and to support each other. Alternatively, it can feel slow and laborious compared to a more top-down or stoic ‘I’ll just do it myself’ approach. But the benefits tend to far outweigh the frustrations of inviting colleagues further into decision-making, planning and carrying out tasks. Multiple studies have shown that collaborative approaches increase healthy working relationships, fostering an environment where trust and good communication grow. And that collaboration supports significant improvements in innovation and business outcomes in general. What good collaboration looks like in practice will vary from team to team and from project to project – it’s worth taking time to do the groundwork around this, as well as considering factors such as whether increased responsibility within a particular project will add pressure to colleagues’ capacity (in this case, it’s worth considering how their time and workload might be protected).
Citizenship
This seems to me like the most nebulous of the 7 Cs, but it offers a valuable opportunity to think beyond the confines of the project or organisation that the socially conscious leader is part of. It’s about the leader, and the team they are part of, connecting to their wider community and society, and considering what they might contribute. How might we utilise the skills and insights that we have learned through leadership development to benefit the communities we are part of? And how might the leadership work that we are doing be part of the change we want to see in the world? It can be helpful to step back from time to time and look at the bigger picture, re-establish our goals and vision, and decide whether we need to make any changes or new commitments in service of this. However, I do acknowledge that this can feel like a huge responsibility, and am conscious of a need to work within our sphere of influence without over-stretching ourselves. It seems possible to hold both positions though – we can aim to make change on a realistic, sustainable level that protects us from burnout, while considering how this links to the bigger picture and how we might best use our skills to be a small part of bigger changes.